Chapter 10: Friendship Relationships
When you hear the words “friend” or “friendship,” what comes to mind? In today’s society, the words “friend” and “friendship’ can refer to a wide range of different relationships or attachments. We can be a “friend” of a library, museum, opera, theatre, etc.… We can be a “friend” to someone “in need.” We can “friend” thousands of people on social media platforms like Facebook. We can develop friendships with people in our day-to-day lives at work, in social groups, at school, at church, etc.… Some people see their parents/guardians, spouses, and siblings as “friends.” Many of us even have one or more “best friends.” So, when we look at all of these different areas where we use the word “friend,” do we mean the same thing? For this chapter, we’re going to delve into the world of interpersonal friendships, which at least takes a few items off of our list (e.g., libraries, museums, operas, etc…), but we’re still left with a term that is very difficult to define, which is why you’ll be exposed to several different theories throughout the chapter.
Beverley Fehr was one of the first scholars to note the problem related to defining the term “friendship,” “Everyone knows what friendship is – until asked to define it. There are virtually as many definitions of friendship as there are social scientists studying the topic.”1 Table 1 presents some sample definitions that exist in the literature for the terms “friend” or “friendship.”
| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Anthropological | “A friendship-like relationship is a social relationship in which partners provide support according to their abilities in times of need, and in which this behavior is motivated in part by positive affect between partners.”2 |
| Clinical Psychology | “[S]omeone who likes and wishes to do well for someone else and who believes that these feelings and good intentions are reciprocated by the other party.”3 |
| Dictionary | “The emotions or conduct of friends; the state of being friends.”4 |
| Evolutionary | “Friendship is a long-term, positive relationship that involves cooperation.”5,6 |
| Friendship as Love | “The etymology of word friend connects its meaning with love, freedom and choice, suggesting an ideal definition of friendship as a voluntary relationship that includes a mutual and equal emotional bond, mutual and equal care and goodwill, as well as pleasure.”7 |
| Legal | “Friendship is a word of broad and varied application. It is commonly used to describe the undefinable relationships which exist not only between those connected by ties of kinship or marriage, but as well between strangers in blood, and which vary in degree from the greatest intimacy to an acquaintance more or less casual.”8 |
| Personality | “[V]oluntary, mutual, flexible, and terminable; relationships that emphasize equality and reciprocity, and require from each partner an affective involvement in the total personality of the other.”9 |
| Philosophy | “[A] distinctively personal relationship that is grounded in a concern on the part of each friend for the welfare of the other, for the other’s sake, and that involves some degree of intimacy.”10 |
| Social Psychology | “[V]oluntary or unrestrained interaction in which the participants respond to one another personally, that is, as unique individuals rather than as packages of discrete attributes or mere role occupants.”11 |
Table 10.1 Defining Friendship
As you can see, there are several different ways that scholars can define the term “friendship.” So, we must question whether defining the term “friendship” is the best way to start a discussion of this topic.

10.1 Friendship Relationships
Learning Objectives
- Evaluate Rawlins’ friendship characteristics.
- Analyze the importance of communication in the formation of friendships.
- Appraise Rawlins’ dialectical approach to friendships.
In a 2017 book on the psychology of friendship, Michael Monsour asked the different chapter authors if they planned on defining the term “friendship” within their various chapters.12 Monsour found that the majority of the authors planned on not defining the term “friendship,” but instead planned on identifying characters of the term “friendship.” We point this out because defining “friend” and “friendship” isn’t an easy thing to do. We all probably all see our friendships as different or unique, which is one of the reasons why defining the terms is so hard. For our purposes in this chapter, we’re going to go along with the majority of friendship scholars and not provide a strict definition for the term friend.
Friendship Characteristics
William K. Rawlins, a communication scholar and one of the most influential figures in the study of friendship, argues that friendships have five essential characteristics that make them unique from other forms of interpersonal relationships: voluntary, personal, equality, involvement, and affect (Figure 10.2).13

All Friendships are Essentially Voluntary
There’s an old saying that goes, “You can’t choose your family, but you can choose your friends.” This saying gets at the basic idea that friendship relationships are voluntary. Friendships are based out of an individual’s free will to choose with whom to have a friendship. We go through our lives constantly making decisions to engage in a friendship with one person and not engage in a friendship with another person. Each and every one of us has our reasons for friendships. For example, one of our coauthors originally established a friendship with a peer during graduate school because they were the two youngest people in the program. In this case, the friendship was initiated because of demographic homophily but continues almost 20 years later because they went on to establish a deeper, more meaningful relationship over time. Take a second and think about your friendships. Why did you decide to engage in those friendships? Of course, the opposite is also true. We meet some people and never end up in friendship with them. Sometimes it’s because you’re not interested or the other person isn’t interested (voluntariness works both ways). We also choose to end some friendships when they are unhealthy or no longer serve a specific purpose within our lives.
Friendships are Personal Relationships that are Negotiated Between Two Individuals
The second quality of friendships is that they are personal relationships negotiated between two individuals. In other words, we create our friendships with individuals, and we negotiate what those relationships look like with that other individual. For example, let’s imagine you meet a new person named Kris. When you enter into a relationship with Kris, you negotiate what that relationship will look like with Kris. If Kris happens to be someone who is transgendered, you are still entering into a relationship with Kris and not everyone who is transgendered. Kris is not the ambassador for all things transgendered for us, but rather a unique individual we decide we want to be friends with. Hence, these are not group relationships; these are individualized, personal relationships that we establish with another person.
Friendships Have a Spirit of Equality
The next characteristic of friendships is a spirit of equality. “Although friendship may develop between individuals of different status, ability, attractiveness, or age, some facet of the relationship functions as a leveler. Friends tend to emphasize the personal attributes and styles of interaction that make them appear more or less equal to each other.”14 Now, it’s important to note that we’re not always talking about a 50/50 split in everything is what makes a friendship equal. Friendships ebb and flow over time as the desires, needs, and interests change. For example, it’s perfectly possible for two people from very different social classes to be friends. In this case, the different social classes may put people at an imbalance when it comes to financial means, but this doesn’t mean that the two cannot still have a sense of equality within the relationship. Here are some ways to ensure that friendships maintain a spirit of equality:
- Both friend’s needs and desires are important, not just one person’s.
- Both friends are curious about their friend’s personal lives away from the friendship.
- Both friends show affection in their ways.
- Both friends demonstrate effort and work in the relationship.
- Both friends encourage each other’s goals and dreams.
- Both friends are responsible for mutual happiness.
- Both friends decide what activities to pursue and how to have fun.
- Both friends are mutually engaged in conversations.
- Both friends carry each other’s burdens.
- Both friends desire for the relationship to continue and grow.
Friendships Have Mutual Involvement
The fourth characteristic of friendships is that they involve mutual involvement. For friendships to work, both parties have to be mutually engaged in the relationship. Now, this does not mean that friends have to talk on a daily, weekly, or even monthly basis for them to be effective. Many people establish long-term friendships with individuals they don’t get to see more than once a year or even once a decade. For example, the father of one of the authors has a group of friends from high school. His friends and their spouses pick a location, and they all meet up once a year for a week together. For the rest of the year, there are occasional emails and Facebook posts, but they don’t interact much outside of that. However, that once a year get together is enough to keep these long-term (70+ years) friendships healthy and thriving.
As you can see, the concept of “mutual involvement” can differ from one friendship pair to another. Different friendship pairs collaborate to create their sense of what it means to be a friend, their shared social reality of friendship. “This interpersonal reality evolves out of and furthers mutual acceptance and support, trust and confidence, dependability and assistance, and discussion of thoughts and feelings.”15 One of the reasons why defining the term “friendship” is so difficult is because there are as many friendship realities as there are pairs of friends. Although we see common characteristics across them (as we’re discussing here), it’s important to understand that within these characteristics are many ways these get exhibited.
Friendships Have Affective Aspects
The final characteristic of friendships is the notion of affect. Affect refers to “any experience of feeling or emotion, ranging from suffering to elation, from the simplest to the most complex sensations of feeling, and from the most normal to the most pathological emotional reactions. Often described in terms of positive affect or negative affect, both mood and emotion are considered affective states.”16 Built into the voluntariness, personal, equal, and mutually involved nature of friendships is the inherent caring and concern that we establish within those friendships, the affective aspects. Some friends will go so far as to say that they love each other. Not in the eros or romantic sense of the term, but instead in the philia or affectionate sense of the term. People often use the term “platonic” love to describe the love that exists without physical attraction based on the writings of Plato. However, Aristotle, Plato’s student, believed that philia was an even more profound form of dispassionate, virtuous love that existed in the loyalty of friends void of any sexual connotations.
All friendships are going to have affective components, but not all friendships will exhibit or express affect in the same ways. Some friendships may exhibit no physical interaction at all, but this doesn’t mean they are not intimate emotionally, intellectually, or spiritually. Other friendships could be very physically affective, but have little depth to them in other ways. Every pair of friends determines what affect will be like within that friendship pairing. However, both parties within the relationship must have their affect needs met. Hence, people often need to have conversations with friends about their needs for affection.
Communication and Friendship Formation
Now that we’ve explored the five basic characteristics of friendships, let’s switch gears and focus on communication and friendships. This entire chapter is about communication and friendships, but we’re going to explore two communication variables that do impact the formation of friendships.
Communication Competence
Previously in this book, we talked about the notion of communication competence. For our purposes, we used the definition from John Wiemann, “the ability of an interactant to choose among available communicative behaviors in order that he [she/they] may successfully accomplish his [her/their] own interpersonal goals, while maintaining the face and line of his [her/their] fellow interactants within the constraints of the situation.”17 Not surprisingly, an individual’s communication competence impacts their friendships. Kenneth Rubin and Linda Rose-Krasnor took communication competence a step further and referred to social communicative competencies, “ability to achieve personal goals in social interaction while simultaneously maintaining positive relationships.”18 The most common place where we exhibit social competencies is within our friendships. Throughout our lifespans, we continue to develop our social communicative competencies through our continued interactions with others. However, individuals with lower levels of competency will have problems in their day-to-day communicative interactions. Analisa Arroyo and Chris Segrin tested this idea and found that individuals who reported having lower levels of communication competence were less satisfied in their friendships. Furthermore, individuals who rated a specific friend as having lower levels of communication competency reported lower levels of both friendship satisfaction and commitment. So right off the bat people with lower levels of communication competence are going to have problems in their communicative interactions with friends.
Communication Apprehension
Another variable of interest to communication scholars has been communication apprehension (CA). We also know that peers tend to undervalue their quieter peers, generally seeing them as less credible and socially attractive.19 In a study examining friendships among college students, college students indicated how many people they would classify as “good friends.”20 For people with higher levels of CA, over a third of the quiet people reported having no good friends at all. No students with low or average levels of CA reported having no good friends. Over half of high CA individuals also reported family members as being their good friends (e.g., siblings, parents/guardians, cousins, etc.). Less than 5% of individuals with low or average levels of CA mentioned relatives. Ultimately, we know it’s harder for people with higher levels of CA to establish relationships and keep those relationships growing. Furthermore, individuals with higher levels of CA are less satisfied with their communicative interactions with friends.21
As you can see, both communication competence and CA are important precursors in communication that impact the establishment of effective friendship relationships.
Dialectical Approaches to Friendships
Earlier in this book, we introduced you to the dialectical perspective for understanding interpersonal relationships. William K. Rawlins proposed a dialectical approach to friendships.22 The dialectics can be broken down into two distinct categories: contextual and interactional.
Contextual Dialectics
The first category of dialectics is contextual dialectics, which are dialectics that stem out of the cultural order where the friendship exists. If the friends in question live in the United States, then the prevailing social order in the United States will impact friendship; however, if the friends are in Malaysia, then the Malaysian culture will be the prevailing social order that impacts the friendship. There are two different dialectics that Rawlins labeled as contextual: private/public and ideal/real.
Private/Public
The first friendship dialectic is the private/public dialectic. Let’s start by examining the public side of friendships in the United States. Sadly, they aren’t given much credence in the public space. For example, there are no laws protecting friendships. Your friends can’t get health benefits from your job. Religious institutions don’t recognize your friendships. As you can see, we’re comparing friendships here to marriages, which do have religious and legal protections. In fact, in the legal system, the family often trumps friends unless there is a power of attorney or will.
As a significant historical side note, one of the biggest problems many gay and lesbian couples faced before marriage legalization was that their intimate partners were perceived as “friends” in the legal system. Family members could swoop in when Partner A passed and evict and confiscate all of Partner A’s money and property unless there was an iron-clad will leaving the money and property to Partner B. From a legal perspective, marriage equality was very important in ensuring the rights of LGBTQIA individuals and their spouses.
On the opposite end of this dialectic, many friendship bonds are as strong if not stronger than familial or marital bonds. We voluntarily enter into friendships and create our sense of purpose and behaviors outside of any religious or legal context. In essence, these friendships are autonomous and outside of social strictures that define the lines of marital bonds. Instead of having a religious organization dictate the morality of a relationship, friendships ultimately develop their sense of morality that is based within the relationship itself.
Ideal/Real
From the moment we are born, we start being socialized into a wide range of relationships. Friendship is one of those relationships. We learn about friendships from our family, schools, media, peers, etc.…(Remember “enculturation” from Chapter 6?) With each of these different sources of information, we develop an ideal of what “friendship” should be. However, friendships are not ideals; they are real, functioning relationships that have plusses and minuses. This dialectic also impacts how we communicate and interact within the friendship itself. If our culture tells us that people must be reserved and respectful in private, then a simple act of laughing with another person could be an outward sign of friendship.
Interactional Dialectics
It’s important to understand that friendships change over time; along with how we interact within those friendships. For communication scholars, Rawlins interactional dialectics help us understand how communicative behavior happens within friendships.23 Rawlins noted four primary communicative dialectics for friendships: independence/dependence, affection/instrumentality, judgment/acceptance, and expressiveness/protectiveness.
Independence/Dependence
First and foremost, friendships are voluntary relationships that we choose. However, there is a constant pull between the desire to be an independent person and the willingness to depend on one’s friend. Let’s look at a quick example. It’s a Friday afternoon, and you’re done with class or work. A movie you’ve wanted to see just came out, so you go and watch a matinee. You decided to engage in behavior without thought of your friend. You acted independently. It’s also possible that you know your friend hates going to the movies, so engaging independent movie watching behavior is very much in line with the norms you’ve established within your friendship.
On the other side, we do depend on our friendships. You could have a friend that you do almost everything with, and it gets to the point that people see you as a duo and are shocked when both of you aren’t together. In these highly dependent friendships, individual behavior is probably very infrequent and more likely to be resented. Now, if you went to the movie alone in a highly dependent friendship, your friend may be upset or jealous because you didn’t wait to see it with her/him/them. Now you may have had the right to engage as an independent person, but a friend in a highly dependent friendship would see this as a violation. Now this story would cause even more friction within the friendship if you had promised your friend to see the movie with her/him/them. You would still be acting independently, but your friend would have a stronger foundation for being upset.
Ultimately, all friendships have to negotiate independence and dependence. As with the establishment of any friendship norm, the pair involved in the relationship needs to decide when it’s appropriate to be independent and when it is appropriate to be dependent. Maybe you need to check-in via text 20 times a day (pretty dependent) or talk on the phone once a year; in both cases, friendships are different and are in constant negotiation. It’s also important to note that a friendship that was once highly dependent can become highly independent and vice versa.
Affection/Instrumentality
The second interaction dialectic examines the intersection of affection as a reason for friendship versus instrumentality (the agency or means by which a person accomplishes her/his/their goals or objectives). As Rawlins noted, “This principle formulates the interpenetrated nature of caring for a friend as an end-in-itself and/or as a means to an end.”24 We already discussed the importance of affection in a friendship, but haven’t examined the issue of friendships and instrumentality. In friendships, the issue of instrumentality helps us understand the following question, “How do we use friendships to benefit ourselves?” Some people are uncomfortable with this question and find the idea of instrumentality very anti-friendship. Ever had a really bad day and all you needed was a hug from your best friend? Well, was that hug a sign of affection (maybe), but you used that friendship to get something you wanted/needed. We all do this to varying degrees within friendships. Maybe you don’t have a washer and dryer in your apartment, so you go to your best friend’s place to do laundry. In that situation, you are using your friend and that relationship to achieve a need that you have (wearing clean clothes).
The problem of instrumentality arises when one party feels that he/she/they are being used and taken for granted within the friendship itself or if one friend stops seeing these acts as voluntary and starts seeing them as obligatory. First, there are times when there is an imbalance in friendships, and one friend feels like their are being taking advantage of by the other. Maybe the friend with the washer and dryer starts realizing that the only time his “friend” really reaches out to see if he’s available to hang out is when the “friend” needs to do laundry. Second, sometimes acts that were initially voluntary become seen as obligatory. In our example, maybe the friend who needs to wash her/his/their clothes starts to see what was once a nice, voluntary gesture as an obligation. If this happens, then the use of the washer and dryer becomes part of the rules of the friendship, which can change the dynamic of the relationship if the person with the washer and dryer isn’t happy about being used in this way.
Judgment/Acceptance
In our friendships, we expect that these relationships are going to enhance our self-esteem and make us feel accepted, cared for, and wanted. On the other hand, interpersonal relationships of all kinds are marked by judgmental messages. Ronald Liang argued that all interpersonal messages are inherently evaluative.25 So, how do we navigate the need to be accepted and the reality of being judged? A lot of this is involved in the negotiation of the friendship itself. Although we may not appreciate receiving criticism from others, Liang argues that criticism demonstrates to another person that we value them enough to judge.26 Now, can criticism become toxic, yes? Maybe you’ve experienced a friend who criticized everything about you. Perhaps it got to the point where it felt that you needed to change pretty much everything about how you look, act, think, feel, and behave just to be “good enough” for your friend. If that’s the case, then that friend is clearly not criticizing you for your betterment but for her/his/their desires.
Expressiveness/Protectiveness
The final interactional dialectic is expressiveness/protectiveness. This dialectic questions the degree to which we want to express ourselves in our friendships while determining how much not to express to protect ourselves. As we discussed earlier in this book, social penetration theory starts with the basic idea that in our initial interactions with others we disclose a wide breadth about ourselves. Still, these are primarily surface level topics (e.g., what’s your major, what are your hobbies, where are you from, etc.). As time goes on, the number of topics we express decreases, but they become more personal (depth). In a friendship relationship, we have to navigate this breadth and depth in deciding what we express and what we protect.
Ultimately, this is an issue of vulnerability. When we open ourselves up to people and express those deeper parts of ourselves, there is an excellent likelihood that disclosure of these areas could cause greater harm to the individual self-disclosing if the information got out. For example, one of the authors had a friendship sour after the authors friend shared with the author’s parents the sexual orientation of that author. That author saw this as a massive violation of the confidentiality of what was self-disclosed in their personal friendship. This friend still speaks to the author’s parents, even decades later, however, the author and that friend still have not spoken after the event where the trust was violated. All friendships are an exploration of what can be expressed and what needs to be protected. We all have some friends that we kind of keep at arm’s length because we know we need to protect ourselves because they tend towards being overly chatty or gossipy. At the same time, we have other friends who get to see the real us as we protect less and less of ourselves in those friendships. No one will ever completely know what’s going on in our heads, but deep friendships probably come the closest and also make us the most vulnerable.
Mindfulness Activity

In a 2018 survey of readers, mindful explored the qualities of good friendships, “(38%) was a friend’s propensity for understanding. Next was 29% for trustworthiness, followed by 13% for compassion. Another 15% of the vote was divided between positivity, generosity, sense of humor, and sharing similar interests and passions. Finally, 5% of respondents named other qualities, such as self-awareness and honesty.”27
For this activity, we want you to think about how you can become more mindful of your friendships. There are three things you can do to be more mindful in your friendships: be present, try something new, and practice compassion and kindness.28 Think about your friendships and answer the following questions:
- When you’re with your friends, are you truly present, or do you let distractions (e.g., your cell phone, personal problems, etc.) get in the way of your interactions?
- How often do you and friends do new things, or are you stuck in a rut doing the same activities over and over again?
- When you’re with your friends, are you mindfully aware of your attention, intention, and attitude? If not, what can you do to refocus yourself to be more present?
Key Takeaways
- William K. Rawlins proposed five specific characteristics of friendships: voluntary (friendships are based on an individual’s free will), personal (we create our friendships with individuals negotiating what those relationships look like with that other individual), equality (friendships have a sense of balance that makes them appear equal), involvement (both parties have to be mutually engaged in the relationship), and affect (friendships involve emotional characteristics different from other types of relationships).
- Two important communication variables impact friendship formation: communication competence and communication apprehension. Individuals who have lower levels of communication competence have fewer opportunities to make friends and actually report lower overall satisfaction with their friendships. Individuals with communication apprehension are less likely to engage in interactions with others, so they have fewer opportunities to engage in friendships. Individuals with high levels of communication apprehension report having fewer friendships and are more likely to list a family member as her/his/their best friend.
- Rawlins’ dialectical approach to communication breaks friendship down into two large categories of dialectical tensions: contextual (private/public & ideal/real) and interactional (independence/dependence, affection/instrumentality, judgment/acceptance, and expressiveness/protectiveness). These dialectical tensions provide friendship scholars a framework for understanding and discussing friendships.
Exercises
- Think about one of your current or past friendships. Examine that friendship using Rawlins’ five characteristics of friendships: voluntary, personal, equality, involvement, and affect.
- How has your communication competence or communication apprehension impacted your ability to develop friendships? Also, what advice would you give to someone who has low levels of communication competence or high levels of communication apprehension on how to form friendships?
- Think about one of your current or past friendships. Use Rawlins friendship dialectics to analyze this friendship (both contextual and interactional). After analyzing your friendship, what do these dialectical tensions tell you about the nature and quality of this friendship?
10.2 Stages and Types of Friendships
Learning Objectives
- Differentiate among Rawlins’ seven stages to friendships.
- Evaluate Matthews three basic types of friendships (patterns to friendship).
- Compare and contrast healthy and unhealthy friendships.
In Stephen Sondheim and George Furth’s musical “Merrily We Roll Along,” the story follows the careers and friendships of three people trying to make in New York City. One song in the show has always stuck out because of its insightful message about friendship, “Hey Old Friends.” In the musical, three friends Mary, Charlie, and Frank get together after not having seen each other for a while. The purpose of the song is to discuss how some friendships can persist even when we aren’t in each other’s lives daily. You can see a clip from the rehearsal at the New York City Center’s Encore’s production starring Celia Keenan-Bolger (Mary), Colin Donnell (Frank) and Lin-Manuel Miranda (Charley).
In this short song, we learn a lot about the nature of this group’s friendship and their enduring desire to be close to one another through the ins and outs of life. This section of the chapter is going to examine the stages that friendships through, the types of friendships we have, and healthy vs. unhealthy friendships.
Stages of Friendships
As we’ve already discussed, friendships are not static relationships with which we’re automatically born. Instead, these relationships are dynamic, and we grow with them. To help us understand how we ultimately form friendships, William Rawlins broke this process into seven stages of friendships (Figure 10.3).29
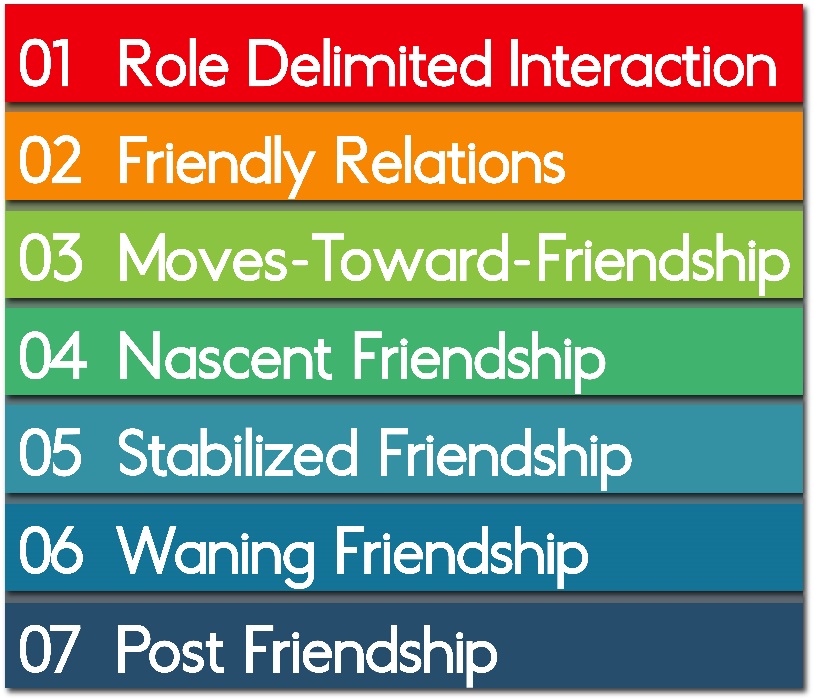
Role Delimited Interaction
The first stage of friendship is called role delimited interaction. The basic idea behind this stage is that we all exist in a wide range of roles within our lives: shopper, salesperson, patient, driver, student, parent/guardian, spouse, etc.… In each of these different roles, we end up interacting with a wide range of different people. For example, imagine you’re just sitting down in a new class in college, and you talk to the stranger sitting next to you named Adilah. In this case, you are both interacting within your roles as students. Outside of those roles and that context, you may never meet and never have the opportunity even to develop a social relationship with this other person. This does not discount the possibility of random, chance encounters with other people. Still, most of our interpersonal relationships (outside of our family) stem from these roles and the communicative contexts they present.
Friendly Relations
From role delimited interaction, we may decide to move to the second stage of friendship, friendly relations. These relations are generally positive interactions, but they still exist within those same roles. In our example, we start chatting with Adilah before the beginning of each class. At this point, though, most of our interactions are still going to be within those roles, so we end up talking about the class, fellow students, the teacher, homework assignments, etc.… Notice that there is not a lot of actual self-disclosure happening within friendly relations. Some people can maintain friendly relations with others for years. For example, you may interact with coworkers, religious association members, neighbors within this type of relationship without them ever progressing to the next stage of friendship. According to Rawlins, friendly relationships move towards friendships because they start to exhibit four specific communication behaviors:
- moves away from what is required in the specific role relationship,
- fewer lines and less stereotyped interaction,
- individual violations of public propriety, and
- greater spontaneity.30
First, we start interacting in a manner that doesn’t resemble the original roles we had. In our example, we start interacting in a manner that doesn’t resemble the roles of students when they first meet. Second, we move away from lines of communication that are stereotypes for our roles. For example, some possible stereotyped lines for two students could include, “what did you think of the homework;” “did you break your book with you today;” “see you next class;” etc… In each of these lines, we enact dialogue that is expected (or stereotyped) within the context of the class itself. Third, more of our normal selves will start to seep into our interactions, which are called violations of public propriety. Maybe one day Adilah turns to you before class, saying, “That reading for homework was such a waste of time.” In this case, Adilah is giving you a bit more insight into who she is as a person “These violations of public propriety single an individual out as having an essential side which is not so easily circumscribed by the protocol of a situation.”31 Lastly, we see increased spontaneity in our interactions with the other person. Over time, these interactions, although still interacting within their formal roles, take on more social and less formalized tones. Maybe one day Adilah tells you a joke or shares a piece of gossip she heard. In this case, Adilah she’s starting to be more spontaneous and less structured in her interactions with us.
Moves-Toward-Friendship
At some point, people decide to interact with one another outside of the roles they originally embodied when they initially met. This change in roles is a voluntary change. In our example, maybe one day Adilah invites you to get coffee after class, and then another day, you ask her to get lunch before class. Although it’s possible that a single step outside of those roles could be enough that a friendly relation is moving towards a friendship, there is generally a sequence of these occurrences. In our example here, Adilah may have made the first move inviting us to coffee, but we then reciprocated later by asking her to lunch. In both of these cases, we are starting to step outside of the original friendly relation and changing the nature of our original interactions.
Nascent Friendship
When one enters into the nascent stage of friendship, the friends are no longer interacting within their original roles, and their interactions do follow the stereotypes associated with those roles. Eventually, we start to develop norms for how we communicate with this other person that is beyond those original roles and stereotypes. Ultimately, this stage is all about developing those norms. We develop norms for what we talk about, when we talk, and how we talk. Maybe Adilah makes it very clear that she doesn’t want to talk about politics or religion, and we’re perfectly OK with that. Maybe we keep the bulk of our interaction before and after class, or we start having lunch together before class or coffee after class. The norms will differ from friendship to friendship, but these norms allow us to set parameters on the relationship in this early stage. These norms are also important because keeping them demonstrates that we can be trusted. And when we show we can be trusted over time, the level of intimacy we can develop within our relationship also increases.
It’s also during this period that others start to see you more and more as a pair of friends, meaning external forces may begin to impact the development of your friendship as well. In our case, maybe Adilah has a sister who also goes to the school, so she starts hanging out with both of you from time to time. Maybe we have a significant other, and he/she/they start hanging out as well. Even though we may have these distractions, we must keep faithful to the original friendship. For example, if we start spending more time with Adilah’s sister than Adilah, then we aren’t faithful to the original friendship. Lastly, our friendship crystalizes, and others start to see you as a pair or “duo.” On the TV show Survivor, being seen as a “duo” early in the competition can be seen as a threat because it indicates a stronger bond and commitment. You can see where this might come from since it’s natural to have a stronger bond with a person at this stage than someone with whom you are just an acquaintance of and to whom you are friendly (friendly relations stage).
Stabilized Friendship
Ultimately nascent friendships evolve into stabilized friendships through time and refinement. It’s not like one day you wake up and go, “My friendship has stabilized!” It’s much more gradual than that. We get to the point where our developed norms and interaction patterns for the friendship are functioning optimally for both parties, and the friendship is working smoothly. In nascent friendships, the focus is on the duo and developing the friendship. In stabilization, we often bring in new friends. For example, if we had found out that Adilah had coffee with another person from our class during the nascent stage of friendship, we may have felt a bit hurt or jealous by this “outsider” intruding on our growing friendship.” As stabilized friends, we realize that Adilah having coffee with someone else isn’t going to impact the strength of the relationship we already have. If anything, maybe Adilah will find other friends to grow the friendship circle. However, like any relationship, both parties still must make an effort to make the friendship work. We need to reaffirm our friendships, spend time with our friends, and maintain that balance of equity we discussed earlier in this chapter).
Rawlins also notes that friendships in the stabilized stage can represent three different basic patterns: active, dormant, and commemorative.32 Active friendships are ones where there is a negotiated sense of mutual accessibility and availability for both parties in the friendship. Dormant friendships “share either a valued history or a sufficient amount of sustained contact to anticipate or remain eligible for a resumption of the friendship at any time.”33 These friends may not be ones we interact with every day, but the friendship is still very much alive and could take on new meaning and grow back into an active friendship if the time arises. And commemorative friendships are ones that reflect a specific space and time in our lives, but current interaction is minimal and primarily reflects a time when the two friends were highly involved in each other’s lives. With commemorative friendships, we still see ourselves as friends even though we don’t have the consistent interaction that active friendships have.
In a study conducted by Sara LaBelle Scott Myers, the researchers set out to determine what types of relational maintenance strategies people use to keep their friendships going across the three different types of friendship patterns (active, dormant, & commemorative).34 Using the seven relational maintenance behaviors noted by Laura Stafford (positivity, understanding, self-disclosure, relationship talks, assurances, tasks, and networks),35 the researchers recruited participants over the age of 30 to examine the intersection of relational maintenance and friendship types. All three friendship types engaged in positivity, relational talks, and networks to some degree. No differences were seen in relational maintenance strategies between active and dormant friendships nor dormant friendships and commemorative friendships. However, active friendships were more likely to use understanding, self-disclosure, assurances, and tasks to maintain their friendships than commemorative friendships.
Waning Friendship
Unfortunately, some friendships will not last. There are many reasons why friendships may start to wane or decrease in importance in our lives. There are three primary reasons Rawlins describes for why this happens: “an overall decline in affect, an individual or mutual decision to let it wane based on identifiable dissatisfaction with the relationship, or a significant, negative, relational event which precipitates an abrupt termination of the friendship.”36 First, some relationships wane because there is a decrease in emotional attachment. Some friends stop putting in the time and effort to keep the friendship going, so it’s not surprising that there is a decrease in emotional attachments. Second, both parties may become dissatisfied with the relationship and decide to take a hiatus or spend more time with other friends. Lastly, something could happen, a relationship destroying event. You find out that Adilah had an affair with your romantic partner. Adilah broke a promise to you or told someone one of your secrets. Adilah started yelling at you for no reason and physically assaulted you.
There is a wide range of different events that could end a friendship. In a study conducted by a team of researchers led by Amy Janan Johnson, the researchers interviewed college students about why their friendships had terminated.37 The most common reasons listed for why relationships fell apart were 1) romantic partner of self or friend, 2) increase in geographic distance, 3) conflict, 4) not many common interests, 5) hanging out with different groups or different friends, and 5) other. Now, females and males in the study did report differences in the likelihood that these five reasons led to deterioration. Females reported that conflict was a greater reason for friendship deterioration than males. And males reported not having many common interests was a greater reason for friendship deterioration than females. Females and males did not differ in the other three categories. It’s important to note, that while this set of findings is interesting, it was conducted using college students, so it may not apply to older adults.
Post-Friendship
The final stage of the friendship is what happens after the friendship is over. Even if a friendship ended on a horrible note, there are still parts of that friendship that will remain with us forever. That friendship will impact how we interact with friends and perceive friendships forever. You may even have symbolic links to your friends: the nightclubs you went to, the courses you took together, the coffee shops you frequented, the movies you watched, etc.… all are links back to that friendship. It’s also possible that the friendship ended on a positive note and you still periodically say hello on Facebook or during the holidays through card exchanges. Just as all friendships are unique, so are their experiences of post-friendship reality.
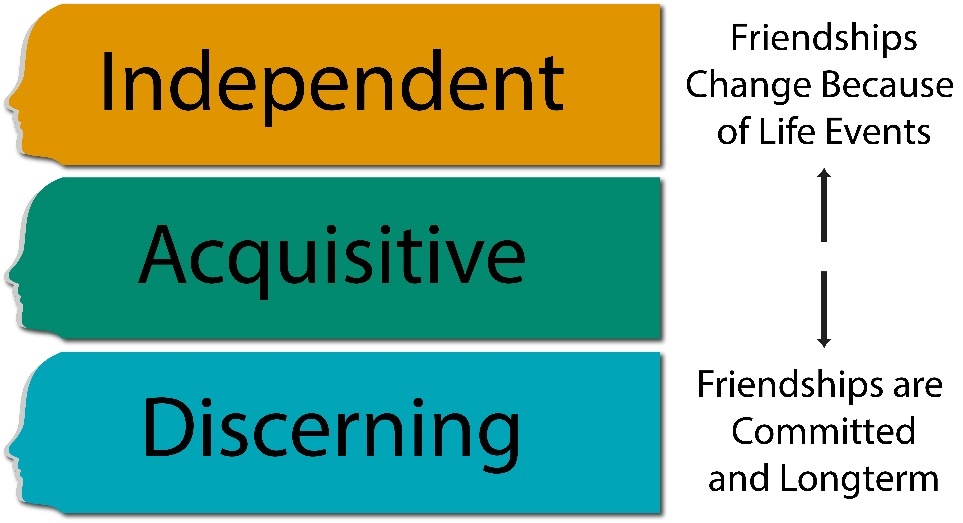
Friendship Styles
Beyond just the stages of friendship development, different people develop different types of friendship throughout their lifetime. Sarah H. Matthews ultimately noted there were three basic types of friendships that people have: independent, discerning, and acquisitive (as seen in Figure 10.4).38 These “styles” can be viewed better as “patterns” or approaches towards friendship overall.
Independent
In her study, she found that independents often saw their friendships based on specific circumstances in their lives and not necessarily by specific friends. When talking about friends, independents were more likely to about “people they knew” or “people they had known,” not reflecting on specific names. Independents were more likely to mention specific names when they talked about people they were interacting with currently. For example, independents talked about friends during periods of their life (e.g., elementary school, junior high/middle-school, high school, college, etc.) and not about specific people they knew for long periods of life. Matthews argues that independents framed their concepts of friendships regarding major life events. They also never reported having a close, special, or best friend relationships, so during periods of major life events, they didn’t have specific commitments to the people they called “friends.” Independents were also more likely to talk about friends as a general concept instead of specific friends. Comparing independents to the stages of friendship discussed by Rawlins, you can consider these to be more along the lines of “friendly relations.” Matthews chose the term “independents” because it reflects a more autonomous state. “It was clear that most of them were not isolated people, but instead considered themselves to be sufficient unto themselves.”39
Discerning
The second type of friendship discussed by Matthews was the discerning style, which, unlike independents, is marked by a deep connection with a friend or group of friends regardless of changing circumstances in their lives. These friendships are marked by deep commitment and longevity, which also means that when a discerning person loses a friend, they are the most likely experience a deep sense of loss in their lives. Discerners were also more likely to draw clear lines between friendly relations and friendship. Overall, “the discerning identified … only a very few people throughout their lives whom they considered friends. Although not all of these informants had kept these friendships, those who had, valued them highly.”40
Acquisitive
The final friendship style discussed by Matthews is the acquisitive style. Acquisitives are “people who moved through their lives collecting a variety of friendships, allowing circumstances to make possible the meeting of likely candidates, but then, committing themselves to the friendships once they were made, at the very least for the period of time during which they and their friends were geographically proximate.”41 Unlike the independents, acquisitives they discussed having close connections with all of the friends they’ve met, and unlike the discerning, acquisitives were open to developing new friendships throughout their lives. In essence, these individuals develop a strong, core group of friends as they go throughout their lives while acquiring new ones depending on changes within their lives.
Good and Bad Friendships
Another system for understanding friendships is to think of them regarding two basic psychological constructs: health and enjoyment. First, is the relationship a healthy one for you to have. Although this is a concept that is more commonly discussed in romantic relationships, friendships can also be healthy or nonhealthy (Table 10.2).
| Healthy | Unhealthy |
|---|---|
| Mutual respect | Contempt |
| Trust | Suspicion |
| Honesty | Untruthful |
| Support | Hinder |
| Fairness/Equality | Unjust/Inequity |
| Separate Identities | Intertwined Identities |
| Open Communication | Closed Communication |
| Playfulness/Fondness | Sober/Animus |
| Self-Esteem Enhancing | Self-Esteem Destroying |
| Fulfilling | Depressing |
| Acceptance | Combative |
| Affectionate/Loving | Cold/Indifferent |
| Comforting | Stressful |
| Genuine/Benevolent | Manipulative/Exploitive |
| Beneficial | Damaging |
| Healthful | Toxic |
Table 10.2 Healthy vs. Unhealthy Friendships
In addition to the health of a friendship, you must also question if the friendship is something that is ultimately enjoyable to you as a person. Does this friendship give you meaning of some kind? Ultimately, we can break this down into four distinct types of friendship experiences people may have (Figure 10.5).
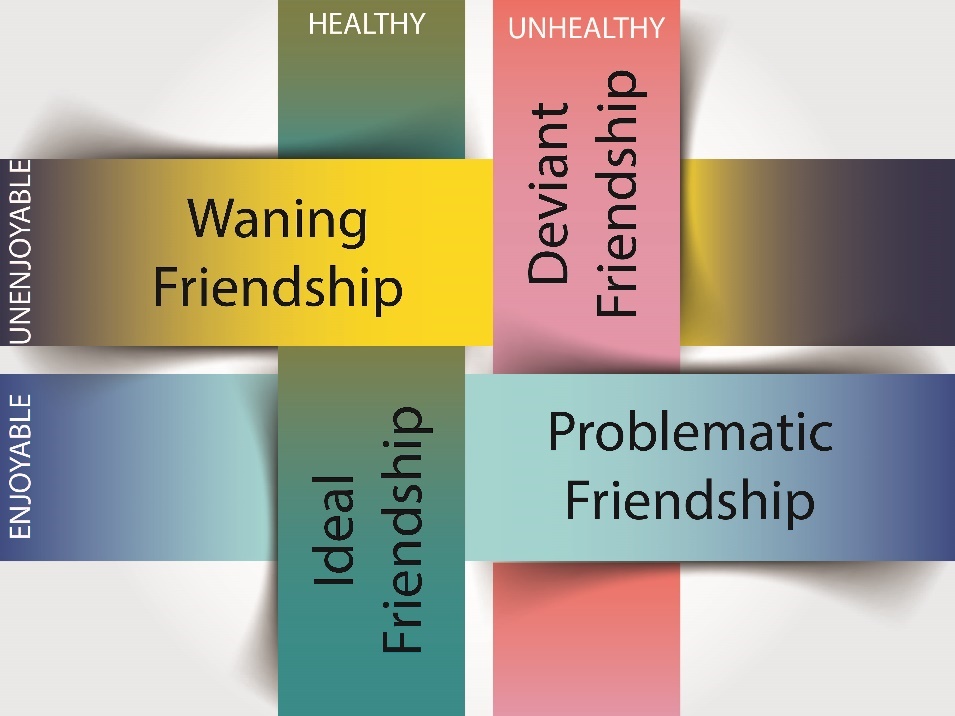
Ideal Friendship
The first category we label as “ideal friends” because these relationships are both healthy and enjoyable. In an ideal world, the majority of our relationships would fall into the category of ideal friendships.
Waning Friendship
The second category we label as “waning friendship” because these friendships are still healthy but not enjoyable anymore. Chances are, this friendship was an ideal friendship at some point and has started to become less enjoyable over time. There’s a wide range of reasons why friendships may stop being enjoyable. It’s possible that you no longer have the time to invest in the friendship, so you find yourself regretting the amount of time and energy that’s necessary to keep the friendship floating.
Problematic Friendship
The third category of friendship, which we classify as problematic friendships, is tricky because these are enjoyable, but they are not healthy for us. Ultimately, the friend we have could be a lot of fun to hang out with, but they also could be more damaging to us as people. Instead of supporting us, they make fun of us. Instead of treating us as equals, they hold all the power in the relationship. Instead of being honest, we always know they’re lying to us. Ultimately, we must question why we decide to stay in these relationships.
Deviant Friendship
The final category of friendships we may have is deviant friendships, more commonly referred to as toxic friendships. For our purposes here, we use the term “deviant” because it refers to any behavior that violates behavioral norms. In this case, any friendship situation that is clearly outside the parameters of what is a healthy and enjoyable friendship is not the norm. Unfortunately, sometimes people get so stuck in these friendships that they stop realizing that these friendships aren’t normal at all. Others may think that their deviant friendships are the only kinds of friendships they can get and/or deserve. It’s entirely possible that a deviant friendship started as perfectly healthy and normal, but often these were somewhat problematic in their early stages and eventually progressed into fully deviant friendships.
Deviant Friends:
- Use criticism and insults as weapons.
- Use guilt to get you to cave-in to their desires and whims.
- Immediately assume you’re lying (probably because they are).
- Disclose your personal secrets.
- Are very gossipy about others, and are probably gossipy about you as well.
- Only care about their own desires and needs.
- Use your emotions as weapons to attack you psychologically.
- Pass judgment on you and your ideas based on their own with little flexibility.
- Are stuck up and only really turn to you when they need you.
- Can be obsessively needy, but then are very hard to please.
- Are inconsistent, so predicting how they will think or behave can be very hard if not impossible.
- Put you in competition with their other friends for affection and attention.
- Conversations tend to be all about them and their desires and needs.
- Make you feel that being your friend is a chore for them.
- Make you feel as if you’ve lost control over your own life and choices.
- Cross major relationship boundaries and violate relationship norms without apology.
- Express their jealousy of your other friendships and relationships.
Key Takeaways
- Rawlins proposed that friendships go through seven distinct stages. The first stage, role delimited interaction, is where we interact with a broad range of people within specific roles we play in life. The second stage, friendly relations, occurs when we have continuous positive interactions with someone, but the interactions still exist within those same roles. The third stage, moves-toward-friendship, occurs when people decide to interact with one another outside of the roles they originally embodied when they initially met. The fourth stage, nascent friendship, occurs when the friends are no longer interacting within their original roles, and their interactions do follow the stereotypes associated with those roles. The fifth stage, stabilized friendship, reflects friendships that have developed norms and interaction patterns that are functioning optimally for both parties, and the friendship is working smoothly. The sixth stage, waning friendship, occurs when a friendship decreases in importance in our lives. The final stage, post-friendship, occurs after a friendship has been terminated.
- Sarah H. Matthews proposed three basic types of (or patterns towards) friendships that people have: independent, discerning, and acquisitive. Independents see friendships based on specific circumstances in their lives and not necessarily by specific friends. Discerning friendships are marked by a deep connection with a friend or group of friends regardless of changing circumstances in their lives. Lastly, acquisitive individuals develop a strong, core group of friends as they go throughout their lives while acquiring new ones depending on changes within their lives.
- To understand health versus unhealthy friendships, it’s also important to consider whether an individual finds that relationship enjoyable or unenjoyable. People who are in a healthy and enjoyable friendship are in ideal friendships. Individuals who are in a healthy friendship that is unenjoyable are in waning friendships. People who are in unhealthy friendships that are enjoyable are in problematic friendships. Lastly, people who are in unhealthy friendships that are unenjoyable are in deviant friendships.
Exercises
- Think back on a friendship that you no longer have. Take that friendship through all seven of Rawlins’ friendship stages. How did you decide when the friendship entered into a new stage?
- Think about your patterns of friendships in your life. Based on the information you learned from Matthews, what type of friendship style do you have? What made you decide that this friendship style most accurately reflects your approach to friendships?
- Thinking about the intersection of healthy friendships and enjoyability, think of one friendship from your own life (past or present) that fits into each category. After coming up with four friendships, differentiate among the four friendships and their outcomes.
10.3 Friendships in Different Contexts
Learning Objectives
- Evaluate J. Donald O’Meara five distinct challenges that cross-sex relationships have.
- Define and explain the term “postmodern friendship.”
- Appraise the importance of cross-group friendships.
- Interpret the impact that mediated technologies have on friendships.
So far in this chapter, we’ve explored the foundational building blocks for understanding friendships. We’re now going to break friendships down by looking at them in a few different contexts: opposite sex friendships, cross-group friendships, and mediated friendships.
Opposite Sex Friendships
“Friendship between a woman and a man? For many people, the idea is charming but improbable.”46 William Rawlins originally wrote this sentence in 1993 at the start of a chapter about the problems associated with opposite sex or cross-sex friendships. What do you think? J. Donald O’Meara discusses five distinct challenges that cross-sex relationships have: emotional bond, sexuality, inequality and power, public relationships, and opportunity structure.47,48
Emotional Bond
First, and foremost, in Western society females and males are raised to see the opposite sex as potential romantic partners and not friends. One of the inherent problems with cross-sex friendships is that one of the friends may misinterpret the friendship as romantic. From an emotional sense, the question that must be answered is how do friends develop a deep-emotional or even loving relationship with someone of the opposite sex. Unfortunately, females are more likely to think this is possible than males. William Rawlins did attempt to differentiate between five distinct love styles that could help distinguish the types of emotional bonds possible: friendship, Platonic love, friendship love, physical love, and romantic love.49 First, friendship is “a voluntary, mutual, personal and affectionate relationship devoid of expressed sexuality.”50 Second, Platonic love is an even deeper sense of intimacy and emotional commitment without sexual activity. Third, is friendship love, which is the interplay between friendships and sexual relationships. It’s often characterized by the use of the terms “boyfriend” and “girlfriend” as distinguishing characteristics to denote paired romantic attachments. Fourth, physical love tends to involve high levels of sexual intimacy with love levels of relationship commitment. And finally, there’s romantic love, or a relationship marked by exclusivity with regards to emotional attachment and sexual activity. O’Meara correctly surmises that the challenge for cross-sex friendships is finding that shared sense of love without one partner slipping into one of the other four categories of love because often the emotions associated with all five different types of love can be perceived similarly.
Sexuality
As the obvious next step in the progression of issues related to cross-sex friendships is sexuality. Inherent in any cross-sex friendship between heterosexual couples is sexual attraction. Sexual attraction may not be something initial in a relationship. Still, it could develop further down the line and start to blur the lines between someone’s desire for friendship and a sexual relationship. In any cross-sex friendship, there will always be a latent or manifested sexual attraction that is possible. Even if one of the parties involved in the friendship is completely unattracted to the other person, it doesn’t mean that the other friend isn’t sexually attracted. As such, like it or not, there will always be the issue of sexuality in cross-sex friendships once people hit puberty. Now it’s perfectly possible that both parties within a friendship are mutually sexually attracted to each other and decide openly not to explore that path. You can find someone sexually attractive and not see them as a viable sexual or romantic partner. For example, maybe you both decide not to consider each other viable sexual or romantic partners because you’re already in healthy romantic relationships, or you may realize that your friendship is more important.
Inequality and Power
We live in a society where men and women are not treated equally. As such, there will always be a level of inequality and power-imbalance created by our society that exist between people in cross-sex friendships. It filters into the relationship expectations, norms, and privileges of that relationship. That power and the influences it has can be overt or covert, known or unknown.
Public Relationships
The next challenge for cross-sex friendships involves the public side of friendships. The previous three challenges were all about the private inner workings of the friendship between a female and a male (internal side). This challenge is focused on public displays of cross-sex friendships. First, it’s possible that others will see a cross-sex friendship as a romantic relationship. Although not a horrible thing, this could give others the impression that a pair of friends are not available for romantic relationships. Or if one of the friends is seen on a date, that the friend is clearly cheating on her/his/their significant other. Second, it’s possible that others won’t believe the couple as “simply being friends.” This consistent devaluing of cross-sex friendships and the favoring of cross-sex romantic relationships in our society puts a lot of stress on cross-sex friendships. This devaluating of friendships over romantic relationships can also be seen as a tool to delegitimize cross-sex friendships. Third, it’s possible that others may question the sexual orientation of the individual’s involvement in the opposite sex friendship. If a male is in a friendship relationship with a female, he may be labeled as gay or bisexual for not turning that cross-sex friendship into a romantic one. The opposite is also true. Lastly, public cross-sex friendships can cause problems for cross-sex romantic partners. Although not always the case, it may be very difficult for one member of a romantic relationship to conceive that their partner is in a close friendship relationship with the opposite sex that is not romantic or sexual. For individuals who have never experienced these types of emotional connections, they may assume that it is impossible and that the cross-sex friends are just “kidding themselves.” Another possible problem for romantic relationships is that the significant other becomes jealous of the cross-sex friend because they believe that, as the significant other, they should be fulfilling any role seen as being met by the cross-sex friend.
Note that many of the challenges in this section have an underlying component of compulsory heterosexuality. Another word for compulsory is mandatory. Therefore, compulsory heterosexuality is the social imposition of a singular sexual orientation, in this case heterosexuality, which a culture expects and/or rewards. This includes the idealization of one narrative, that of heterosexual orientation, heterosexual romance, and heterosexual marriage only. Compulsory heterosexism is also referred to as “heteronormativity.” Again, this can be seen and endorsed throughout numerous societal institutions (media, laws, religious teachings, societal privileges, etc.). Institutions are dynamic and ever-evolving, albeit, sometimes slowly. These cultural norming practices and stereotypes can harm all, but especially those members in the underrepresented groups. Here are two examples: 1) showing unbalanced expectations within the dominant group; two woman can go to the movie theatre and sit right next to each other, while some men doing the same might feel compelled to put an extra seat between them. 2) On the underrepresented group side of things and the potential harm compulsory heterosexuality can cause; two perceived gay or lesbian individuals might not feel safe hanging out together in public because they don’t know if their lives will be threatened or even taken because of their perceived sexual orientation. Lives have been taken. That’s one unfortunate cost and symptom of compulsory heterosexuality. Regardless of your sexual orientation, it’s important to understand how these cultural perceptions and privileges of the dominant group influence and affect the underrepresented group.
Opportunity Structure
The final challenge described by O’Meara was not part of the original four but was described in a subsequent article.51 This question is primarily focused on how individuals find opportunities to develop cross-sex friendships. A lot of our social lives are divided by gender and segregated by sex: females and males. Girls had Girl Scouts and Boys had Boy Scouts. Girls played volleyball and softball while boys played football and baseball. Now, that’s not to say that there aren’t girls who played football or boys who played volleyball, but most of these sports are still highly sex-segregated. As such, when we’re growing up, we are more likely to spend social time with the same-sex. Ultimately, it’s not impossible for cross-sex relationships to develop, but our society is not structured for these to happen naturally in many ways.
Scouts are Changing with the Times
Just as a quick caveat, as of the publication of this book, the Girl Scouts of America is open to transgendered children on a case-by-case basis. However, Boy Scouts of America started accepting girls starting in 2017 and is now called Scouts BSA to show this change to policy. Instead of “boy scouts”, participants are know titled, “scouts.”
Postmodern Friendships
In the previous section, we looked at some of the basic issues of cross-sex friendships; however, a great deal of this line of thinking has been biased by heteronormative patterns of understanding.52 The noted absence of LGBTQIA individuals from a lot of the friendship literature is nothing new.53 However, we have needed newer theoretical lenses to help us break free of some of these historical understandings of friendship. “Growing out of poststructuralism, feminism, and gay and lesbian studies, queer theory has been favored by those scholars for whom the heteronormative aspects of everyday life are troubling, in how they condition and govern the possibilities for individuals to build meaningful identities and selves.”54 By taking a purely heteronormative stance at understanding friendships, friendships scholars built a field around basic assumptions about gender and the nature of gender.55
Friendship scholar Michael Monsour asked a group of friendship scholars about the definition of “friendship” and found there was little to no consensus. How then, Monsour argues, can researchers be as clear in their attempts to define “gender” and “sex” when analyzing same-sex or opposite sex friendships.56 As part of his discussion questioning the nature of gender and sex and how it’s been used by friendship scholars, Monsour provided the following questions for us to consider:
- What does it mean to state that two individuals are in a same-sex or opposite sex friendship and/or that they are of the same or opposite sex from one another?What decision rules are invoked when deciding whether a particular friendship is one or the other?
- Why must the friendship be one or the other?
- If friendship scholars and researchers believe that all friendships are either same–sex or opposite–sex (and it appears that most do), at a minimum there should be agreement about what constitutes biological sex. What biological traits make a person a female or a male?
- Are they absolute? Are they universal?57
- As part of this discussion, Monsour provides an extensive list of areas of controversy related to the terms used for binary gender identity. What about individuals who are intersexed? What about individuals with chromosomal differences outside of traditional XX and XY (e.g., X, Y, XYY, XXX, XXY, etc.)? Heck, there are even some XXmales and XYfemales who develop because of chromosomal structural anomalies SRY region on the Y chromosome.
- What about bisexual, gay, and lesbian people?
- What about people who are transgendered or transsexual?
- What about people who are asexual?
Hopefully, you’re beginning to see that the concept of ascribing same-sex and opposite sex friendships simply based on 46-chromosomal pairs of either XX or XY who are cisgendered and heterosexual may not be the best or most complete way of understanding friendships.
We should also note that research in the field of communication has noted that an individual’s biological sex contributes to maybe 1% of the differences between “females” and “males.”58 So, why would we use the words “same” and “opposite” to differentiate friendship lines when there is more similarity between groups than not? As such, we agree with the definition and conceptualization of the term created by Mike Monsour and William Rawlins’ “postmodern friendships.”59 A postmodern friendship is one where the “participants co-construct the individual and dyadic realities within specific friendships. This co-construction involves negotiating and affirming (or not) identities and intersubjectively creating relational and personal realities through communication.”60 Ultimately, this perspective allows individuals to create their own friendship identities that may or may not be based on any sense of traditional gender identities.
Cross-Group Friendships
As we noted above, research has found that one of the biggest factors in friendship creation is the groups one belongs too (more so for males than females). In this section, we’re going to explore issues related to cross-group friendships. A cross-group friendship is a friendship that exists between two individuals who belong to two or more different cultural groups (e.g., ethnicity, race, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, nationality, etc.). “The phrase, ‘Some of my best friends are…’ is all too typically used by individuals wanting to demonstrate their liberal credentials. ‘Some of my best friends are… gay.’ ‘Some of my best friends are… Black.’ People say, ‘Some of my best friends are…’ and then fill in the blank with whatever marginalized group which they care to exonerate themselves.”61 Often when we hear people make these “Some of my best friends are…” statements, we view them as seriously suspect and question the validity of these relationships as actual “friendships.” However, many people develop successful cross-group friendships.
It’s important to understand that our cultural identities can help us feel that we are part of the “in-group” or part of the “out-group” as well. Identity in our society is often highly intertwined with marginalization. As noted earlier, we also know that males are more likely to align themselves with others they perceive as similar. Females do this as well, but not to the same degree as males. In essence, most of us protect our group identities by associating with people we think are like us, so it’s not surprising that most of our friendships are with people that demographically and ideologically similar to us. And to a certain extent, we judge members of different out-groups based on our ethnocentric perceptions of behavior. For example, some people ask questions like, “why does my Black friend talk about race so much;” “does my friend have to act ‘so’ gay when we’re in public;” or “I like my friend, but does she always have to talk to me about her religion.” In these three instances (race, sexual orientation, and religion), we see examples of judging someone’s communicative behavior based on their own in-group’s communicative behavioral norms and stereotypes. Especially for people who are marginalized, being marginalized is a part of who they are that cannot be separated from how they think and behave. Maybe a friend talks about race because he/she/they are part of a marginalized racial group, so this is their experience in life. “This is actually normal and understandable behavior on the part of these different groups. They are not the ones who make it the focus of their lives. Society—the rest of us—makes race or orientation or gender an issue for them—an issue that they cannot ignore, even if they wanted to. They have to face it every waking moment of their lives.”62 People who live their lives in marginalized groups see this marginalization as part of their daily life, and it’s intrinsically intertwined with their identity.
Many of us will have the opportunity to develop cross-group friendships throughout our lives. As our society becomes more diverse, so has the likelihood of developing cross-group friendships. In a large research project examining the outcomes associated with cross-group friendships, the researchers found two factors were the most important when it came to developing cross-group friendships: racism and exposure to cross-group friendships. First, individuals who are racist are less likely to engage in cross-group friendships.63 Second, actual exposure to cross-group friendships can lead to more intergroup contact and more positive attitudes towards members in those groups.
Ultimately, successful cross-group friendships succeed or fail based on two primary factors: time and self-disclosure.64 First, successful cross-group friendships take time to develop, so don’t expect them to happen overnight. Furthermore, these relationships will take more time to develop as you navigate your cultural differences in addition to navigating the terms of the friendship itself. Now, it’s important that when we use the word “time” here, we are not only discussing both longitudinal time, but also the amount of time we spend with the other person. The more we interact with someone from another group, the stronger our friendship will become.
Second, successful cross-group friendships involve high amounts of self-disclosure. We must be open and honest with our thoughts and feelings. We need to discuss not only the surface level issues in our lives, but we need to have deeper, more meaningful disclosures about who we are as individuals and who we are as individuals because of our cultural groups.
Mediated Friendships
Probably nothing has more radically altered what the words “friend” and “friendship” mean has been the widespread use of social technology. Although the Internet, as such, has been around since 1969 and was consistently used for the exchange of messages all the way through the 1990s, the public didn’t start to become more actively involved with the technology until it became cheap enough to use in one’s daily life. Before December 1996, using the “information superhighway” was limited to tech professionals, colleges and universities, the government, and hobbyists. Before December 1996, the pricing model for Internet use had been similar to that of a telephone subscription. You paid a base rate that allowed you so many hours each month (usually 10) of connected Internet time, and then you paid an additional rate for each subsequent hour. People who were highly active on the Internet racked up enormous bills using the Internet. Of course, this all changed in December 1996 when America Online (AOL) decided to offer its internet service provider to the world for $19.95 per month for unlimited usage. This change in the pricing structure, ultimately led to the first real wave of people jumping online because it was now economically feasible.
The Internet that we all know and love today looks nothing like the landscape of the late 20th Century. So much has changed in the first 20 years of the new millennium about technology and how we use that technology to interact with your friends and family. For our purposes, we’re going to focus on the issue of mediated friendships in this section. We’ll discuss computer-mediated communication, in general, in Chapter 12.
In the earliest days of online friendships, the technology was commonly used to interact with people at larger geographic distances. You met friends in chatrooms or on bulletin boards (precursors to modern social media), and most often, these people were not ones in your town, state, or even country. By 2002, 72% of college students were interacting with their friends online.65 This is the same year Friendster is created, the year before MySpace comes into existence, and a solid two years before Facebook is created (February 4, 2004). So, most interaction in 2002 was through email, instant messaging, and chat rooms. Today we talk less about using the Internet and more about what types of applications people are using on their smartphones (The iPhone came out on June 29, 2007). For example, in 2018, 68% of U.S. adults used Facebook. By comparison, 81% of adults 18 to 29 use Facebook, while only 41% of U.S. adults over the age of 65 are using Facebook.66 What about other common apps, 73% use YouTube, 35% use Instagram, 29% use Pinterest, 27% use Snapchat, 25% use LinkedIn, 24% use Twitter, and 22% use WhatsApp.
All of these different technologies have enabled us to keep in touch with each other in ways that didn’t exist at the beginning of the 21st Century. As such, the nature of the terms “friend” and “friendship” have changed. For example, how does one differentiate between a friend someone has primarily online and a friend someone sees face-to-face daily? Does the type of technology we use help us explain the nature of our friendships? Let’s explore both of these questions.
What’s a Friend?
As mentioned at the very beginning of this chapter, one of the biggest changes to the story of friendships has been the dilution of the term “friendship.” In some ways, this dilution is a result of social networking sites like Friendster, Facebook, Snapchat, Instagram, etc.… Today, we “friend” people on Facebook that we wouldn’t have had any contact with 20 years ago. We have expanded the term “friend” to include everything from casual acquaintances to best friends. When we compare William Rawlins six stages to friendships to how we use the term “friend” in the mediated context, you’ll see that everything from friendly relations to stabilized friendships gets the same generic term, “friend.”67
One Australian writer, Mobinah Ahmad realized that the term “friend” was being widely used and often didn’t fit the exact nature of the relationships she experienced. She created a six stage theory to express how she views the nature of friendships in the time of Facebook. She started by analyzing her 538 “friends” on Facebook. The overwhelming majority of these “friends” really were acquaintances. In fact, of the 538 friends Ahmad had, she claimed that only one of them was a “true friend.”68 Teacher note: See more on Ahmad’s Six Stage Theory around Friendship Acquaintance in the specially noted resource in your D2L course content.
Technologies and Friendships
Today a lot of our interaction with friends is now mediated in some fashion. Whether it’s through phone calls and texts or social media, gaming platforms, Skype, and other interactive technologies, we interact with our friends in new and unique ways. For example, in a study that came out in 2018, found that 60% of today’s teenagers interact with their friends online daily while only 24% saw their friends daily.69 Interacting online with people is fulfilling some of the basic functions that used to be filled through traditional face-to-face friendships for today’s modern teenagers. Teens who spend time interacting with others in an online group or forum say that these interactions played a role in exposing them to new people (74%), making them feel more accepted (68%), figuring out important issues (65%), and helping them through challenging times in life (55%).
But, are all technologies created equal when it comes to friendships? In a study by Dong Liu and Chia-chen Yang, the researchers set out to determine if how we perceive our friendships differs based on the communication technologies we use to interact.70 The researchers examined data gathered from 22 different research samples collected by researchers around the world. Ultimately, the researchers found that there is a difference in how we use technologies to interact with friends. They labeled the two different categories Internet-independent (e.g., calls, texts, etc.) and Internet-dependent (e.g., instant messaging, social networking sites, gaming, etc.). Of the different technologies examined, “Mobile phone-based channels had stronger associations with friendship closeness, suggesting that phone calls and texting were predominantly used with closest associates.”71 As a side note, the researchers did not find sex differences with regard to communication technologies use and friendship intimacy.
Research Spotlight

In 2018, Bree McEwan, Erin Sumner, Jennifer Eden, and Jennifer Fletcher set out to examine relational maintenance strategies on Facebook among friends. Prevopis research by McEwan found that there were three different relational maintenance strategies used by members of Facebook:72
- Social Contact – personalizing messages to specific friends via Facebook.
- Relational Assurances – demonstrating one’s commitment to continuing a relationship on Facebook.
- Response Seeking – sending messages to a large number of people via Facebook in the hopes of getting input from an array of people.
In this study, the researchers found that social contact, relational assurances, and response seeking were all positively related to liking, relational closeness, relationship satisfaction, and relationship commitment.
McEwan, B., Sumner, E., Eden, J., & Fletcher, J. (2018). The effects of Facebook relational maintenance on friendship quality: An investigation of the Facebook Relational Maintenance Measure. Communication Research Reports, 35(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/08824096.2017.1361393
Key Takeaways
- Although there was a historical perception that same-sex friendships were distinctly different, research has shown that there is more overlap between them than there are actual differences.
- Compulsory heterosexuality is the social imposition of a singular sexual orientation, in this case heterosexuality, which a culture expects and/or rewards. This includes the idealization of one narrative: that of heterosexual orientation, heterosexual romance, and heterosexual marriage only. Compulsory heterosexism is also referred to as “heteronormativity.” This can be seen and endorsed throughout numerous societal institutions (media, laws, religious teachings, societal privileges, etc.). Institutions are dynamic and ever-evolving, albeit, sometimes slowly. These cultural norming practices and stereotypes can harm all, but especially those members in the underrepresented groups.
- J. Donald O’Meara proposed five distinct challenges that cross-sex relationships have: emotional bond (males and females are raised to see the opposite sex as potential romantic partners and not friends), sexuality (inherent in any cross-sex friendship between heterosexual couples is sexual attraction), inequality and power (there will always be a fact of inequality and power-imbalance between people in cross-sex friendships created by our society), public relationships (cross-sex friendships are often misunderstood and devalued in our society in favor of romantic relationships), and opportunity structure (our society often makes it difficult for cross-sex friendships to develop).
- Cross-group friendships are an important part of our society. The two factors that have been shown to be the most important when developing cross-sex friendships are time and self-disclosure. First, cross-group friendships take more time to develop as individuals navigate cultural differences in addition to navigating the terms of the friendship itself. Second, effective cross-group friendships are often dependent on the adequacy of self-disclosure. Individuals in cross-group friendships need to discuss not only the surface level issues in our lives, but they need to have deeper, more meaningful disclosures about who they are as individuals.
Exercises
- In your view, what is a postmodern friendship, and why is it an important perspective for communication scholars? Would any of your friendships fall within this framework? Why?
- Think of a time when you’ve had a cross-group friendship. What made it a cross-group friendship? How did this friendship differ from your same-group friendships? How was it similar to your same-group friendships? If you were explaining to another person the importance of cross-group friendships in your own life, what would you tell them?
- Do you think the word “friend” has been devalued through the use of social media? How many people do you label as a “friend” really are acquaintances?
- Read through Mobinah Ahmad’s six stage theory of friendships and acquaintances theory (found under your D2L content for this week). Do you agree with her perspective? Why? How do you see this playing out in your own life?
Key Terms
active friendships
Type of stabilized friendship where there is a negotiated sense of mutual accessibility and availability for both parties in the friendship.
affect
“Any experience of feeling or emotion, ranging from suffering to elation, from the simplest to the most complex sensations of feeling, and from the most normal to the most pathological emotional reactions. Often described in terms of positive affect or negative affect, both mood and emotion are considered affective states.”
commemorative friendships
Type of stabilized friendship that reflects a specific space and time in our lives, but current interaction is minimal and primarily reflects a time when the two friends were highly involved in each other’s lives.
communication competence
“The ability of an interactant to choose among available communicative behaviors in order that he [she/they] may successfully accomplish his [her/their] own interpersonal goals, while maintaining the face and line of his [her/their] fellow interactants within the constraints of the situation.”
contextual dialectics
Friendship dialectics that stem out of the cultural order where the friendship exists.
cross-group friendship
Friendship that exists between two individuals who belong to two or more different cultural groups (e.g., ethnicity, race, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, nationality, etc.).
dormant friendships
Type of stabilized friendship that “share either a valued history or a sufficient amount of sustained contact to anticipate or remain eligible for a resumption of the friendship at any time.”
interactional dialectics
Friendship dialectics that help us understand how communicative behavior happens within friendships
postmodern friendships
Friendship where the “participants co-construct the individual and dyadic realities within specific friendships. This co-construction involves negotiating and affirming (or not) identities and intersubjectively creating relational and personal realities through communication.”
“Any experience of feeling or emotion, ranging from suffering to elation, from the simplest to the most complex sensations of feeling, and from the most normal to the most pathological emotional reactions. Often described in terms of positive affect or negative affect, both mood and emotion are considered affective states.”
Communication that is both socially appropriate and personally effective.
Friendship dialectics that stem out of the cultural order where the friendship exists.
Friendship dialectics that help us understand how communicative behavior happens within friendships
Type of stabilized friendship where there is a negotiated sense of mutual accessibility and availability for both parties in the friendship.
Type of stabilized friendship that “share either a valued history or a sufficient amount of sustained contact to anticipate or remain eligible for a resumption of the friendship at any time.”
Type of stabilized friendship that reflects a specific space and time in our lives, but current interaction is minimal and primarily reflects a time when the two friends were highly involved in each other’s lives.
the institutionalization of heterosexuality across society including the idealization of heterosexual orientation, romance, and marriage.
Friendship where the “participants co-construct the individual and dyadic realities within specific friendships. This co-construction involves negotiating and affirming (or not) identities and intersubjectively creating relational and personal realities through communication.”
Friendship that exists between two individuals who belong to two or more different cultural groups (e.g., ethnicity, race, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, nationality, etc.).
