18 Overview: HyFlex Technology and Frameworks
I. The Empowered Educator and Liberated Learner Frameworks
The Empowered Educator Framework is a set of guiding principles and practices designed to assist educators in effectively integrating digital tools into their classrooms. It emphasizes the importance of technology literacy, effective communication, collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity in promoting student learning in the digital age. This framework can help educators create engaging and meaningful learning experiences that prepare students for success in an increasingly connected and complex world.
- The Empowered Educator Framework aims to help educators be ready to teach in a digital age.
- The Liberated Learner Framework[1] aims to help learners learn in the digital world.
The application of the two frameworks aimed at instructors and students helps improve digitizing the teaching-learning process. Let’s explore how the Empowered Educator Framework integrates technology tools to empower educators and enhance student learning:
- Choosing Educational Technology Tools:
When selecting technology tools, educators should consider three critical areas:
-
- Content: Start with the content you are teaching. What are the learning objectives, and how can technology enhance them?
- Pedagogy: Consider the pedagogical strategies you’ll use to teach the content. How can technology support these strategies?
- Technology: Finally, explore the available technology tools that align with your content and pedagogical goals3.
- Empowered Learners Initiative (ELi):
- The Empowered Learners Initiative (ELi) is a comprehensive three-year commitment by DC Public Schools (DCPS) to close the digital divide and empower every learner through technology1.
- ELi aims to provide students with the tools they need to be 21st-century learners, emphasizing safe and relevant technology use. Key components of ELi include:
- 1:1 Student-to-Device Ratio: Over three years, DCPS ensures that students in grades 3-12 have equitable access to technology devices. In the first year, this ratio is implemented in grades 3, 6, and 9, and gradually expands to other grades in subsequent years.
- Equipping Educators: DCPS provides professional development to teachers, ensuring they have the skills and knowledge needed to support students in leveraging technology for learning.
- Critical Technology Tools: DCPS offers freely available technology tools to every student and teacher in their schools. These tools align with the Empowered Learner Models and support effective technology integration in the classroom1.
- Digital Fluency:
- Digital fluency empowers students to thoughtfully, safely, and effectively use available tools. It includes the ability to use a range of digital tools and transfer that knowledge when exploring, using, or troubleshooting new tools2.
Remember, technology is a powerful tool when used purposefully and thoughtfully. By integrating it effectively, educators can create engaging learning experiences for their students! 🌟123
II. Technology Integration Models: TPACK and SAMR [2]
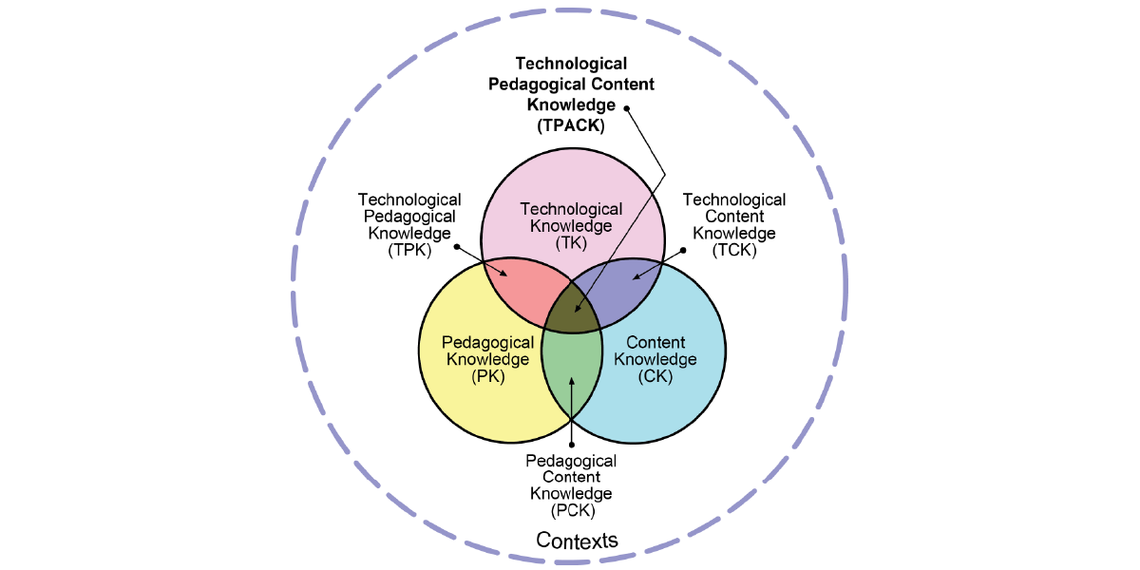
2.1 Technology, Pedagogy, and Content Knowledge (TPACK) Model
TPACK (Mishra & Koehler, 2006) is a model for thinking about teaching through the instructor’s knowledge of the content (Content or CK), the ways they teach the content (Pedagogy or PK), and the technology tools (Technology or TK) they use to support the teaching.
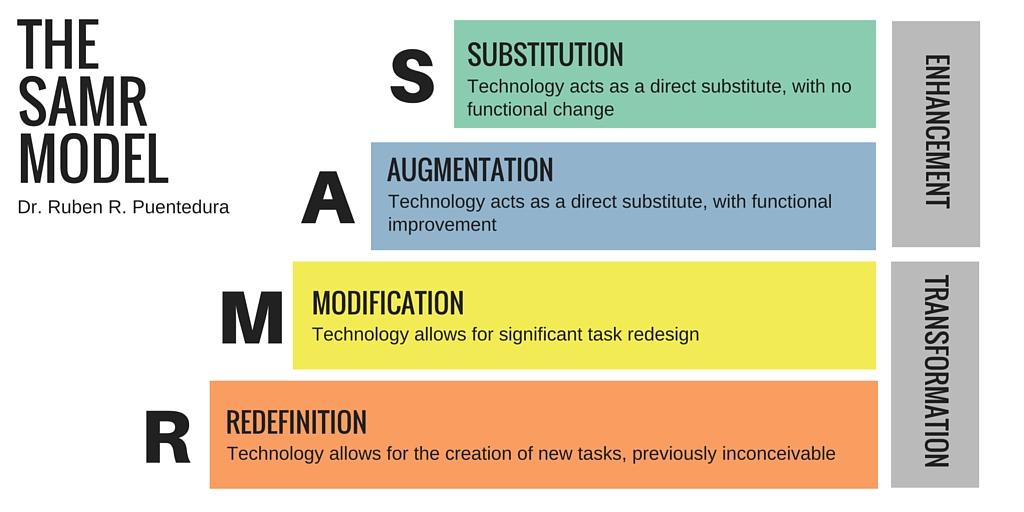
2.2 Substitution, Augmentation, Modification and Redefinition (SAMR) Model
The SAMR model illustrates how technology can be integrated into a task with the intention of modifying learning by transforming from the lower levels to enhancing at the upper levels (Hamilton et. al, 2016).
Using the SAMR model does not require reaching the top level for every task. Each level has its own purpose and deciding which level to achieve depends on the learning outcome of the task and the reasons for integrating the technology.
III. Rubric for selecting Active Learning Technology
Century College uses the Campus Academic Technology Team (CATT), a campus-wide subcommittee that receives nominations on technology tools that faculty select for their teaching and learning process. The CATT also reviews the technology tools with a customized rubric to recommend for adoption by the Information Technology Solutions (ITS) committee.
As the framework for evaluating technologies for active learning, two resources from Educause[3] serve as a good source to consult:
- The Learning Space Rating System (LSRS) addresses the needs of the physical space for active learning. The Learning Space Rating System (LSRS) project provides a set of measurable criteria to assess how well the design of classrooms supports and enables multiple modalities of learning and teaching, especially that of active learning. Please consult the FLEXspace[4] to help you plan, design, implement, maintain, assess, and improve your campus learning spaces.
- Rubric for Active Learning Technology Evaluation Please consult Educause’s sample rubric for technology evaluation. This Rubric-for-eLearning-Tool-Evaluation from Western University of Canada is also helpful
- https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/learner/ ↵
- https://taylorinstitute.ucalgary.ca/resources/SAMR-TPACK#:~:text=Technology%2C%20Pedagogy%2C%20and%20Content%20Knowledge,to%20support%20how%20they%20teach. ↵
- https://er.educause.edu/articles/2022/4/a-rubric-for-selecting-active-learning-technologies ↵
- https://flexspace.org/about/ ↵
