22 Importing Data into Excel
Importing Data from a Database
Learning Objectives
- Get data from a Microsoft Access database.
- Understanding Different File Formats Supported by Excel.
- Importing Data from Text Files.
- Importing Data from Databases.
- Importing Data from Web Sources
Import data from a database
We start this tutorial with a blank workbook. The goal in this section is to connect to an external data source and import that data into Excel for further analysis.
The data we will import describes Olympic Medals and is a Microsoft Access database.
1. Download the OlympicMedals.accb Access database file from the text files and save it where you will be able to find it again for the next steps.
2. In Excel 2016, open a blank workbook.
3. Click DATA > Get Data > From Database> From Microsoft Access Database. The ribbon adjusts dynamically based on the width of your workbook, so the commands on your ribbon may look slightly different from the following screens.
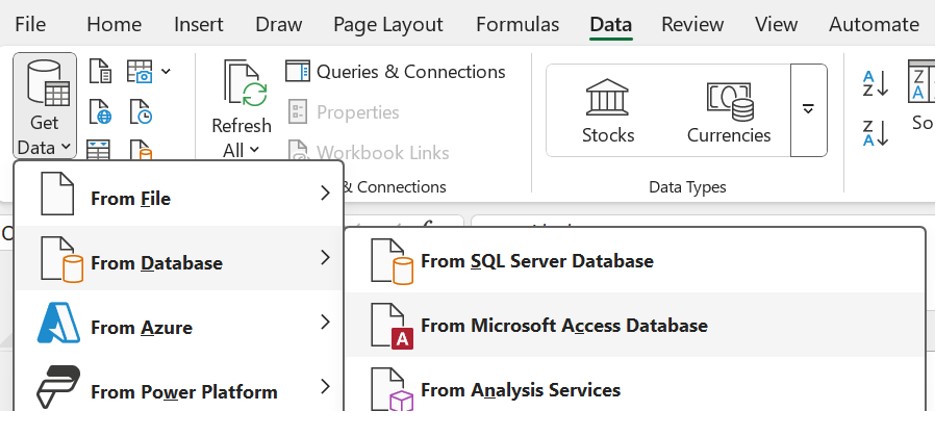
4. Select the OlympicMedals.accdb file you downloaded and click Open. The following Select Table window appears, displaying the tables found in the database. Tables in a database are similar to worksheets or tables in Excel. Check the Enable selection of multiple tables box and select all the tables. Then click OK.

5. The Import Data window appears.
Select the PivotTable Report option, which imports the tables into Excel and prepares a PivotTable for analyzing the imported tables and click OK.

6. Once the data is imported, a PivotTable is created using the imported tables.

With the data imported into Excel, and the Data Model automatically created, you’re ready to explore the data.
Understanding Different File Formats Supported by Excel
Understanding different file formats supported by Excel is crucial for efficient data import and export. Excel provides support for a variety of file formats, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. Acquiring an understanding of these formats will enable you to seamlessly work with diverse data sources. Below is a summary table of the file formats that Excel supports:
| File Format | Description |
| CSV | A file format called Comma-Separated Values, commonly used for data interchange. |
| Text | A plain-text file that stores data in a straightforward format. |
| Databases | Enables you to connect to and import data from different database management systems. |
| Web Sources | Allows importing data from websites through web queries or by connecting to web services. |
| Permits exporting data to a portable document format that is widely used for sharing and preserving document integrity. | |
| Other File Formats | Excel supports numerous other file formats, including XLSX, XLS, XML, and more. |
Considering both the file format and the purpose of import or export, it is essential to select the appropriate format to ensure compatibility and data integrity. Additionally, it is important to stay updated with the latest features and enhancements of Excel in order to fully leverage its capabilities and effectively manage different file formats.
Importing Data from Text Files
When importing data from text files into Excel, follow these steps:
Open Excel and create a new workbook.
Click on the “File” tab and select “Open” to open the file you want to import.
In the “Open” dialog box, locate and select the text file you want to import.
Click on the “Open” button.
Excel will display the Text Import Wizard. Select the appropriate options for your text file, such as the file origin, delimiter, and text format.
Preview the data to ensure it is correctly formatted.
Click on the “Load” button to import the data into Excel.
By following these steps, you can easily import data from text files into Excel for further analysis and manipulation.
Importing Data from Databases
Importing Data from Databases is a crucial task for professionals who need to analyze and manipulate large datasets. Here is a table with different approaches to Importing Data from Databases:
| Approach | Method |
| Direct Connection | Use Excel’s built-in functionality to directly connect to a database and import data. |
| ODBC | Set up an ODBC connection to establish a link between Excel and the database. |
| Query Import | Write a query using SQL, or a database specific language to extract specific data from the database and import it into Excel. |
| Import Wizard | Use Excel’s Import Wizard to setup a connection, specify tables or queries, and import data. |
To ensure smooth Importing Data from Databases, verify that the database credentials are correct, and test the import process with a sample dataset. Remember to properly format the imported data in Excel to ensure it aligns with your analysis needs.
Importing Data from Web Sources
Importing data from web sources is a valuable method to gather information for analysis in Excel, making it essential to know how to incorporate the keywords “Importing Data from Web Sources” in the given text.
When it comes to importing data from web sources, there are several steps to consider:
Identify the data source: Begin by determining the website or webpage that contains the information you need to import into Excel.
Access the data: To input the URL of the webpage, utilize the “From Web” option found in the Data tab of the Excel ribbon.
Select and preview the data: Excel will generate a preview of the data on the webpage, allowing you to choose the specific data elements you wish to import.
Specify import settings: Customize the way the data is imported by utilizing options such as data type, delimiter, headers, and more.
Refresh and update: It is crucial to regularly refresh the imported data to ensure it remains up-to-date. This can be performed manually or automatically at regular intervals.
By effectively following these steps, you can effortlessly import data from web sources into Excel, enabling analysis and manipulation of the data.
Media Attributions
- Renaming an Excel Table
- Table DropDown Sort
- Creating a Multi-level Sort
- Sort Results
- Custom Lists Dialog Box
- Insert PivotTable
- Recommended PivotTables
- GetData From Access
Media Attributions
- GetData From Access
